MORE ABOUT CBD
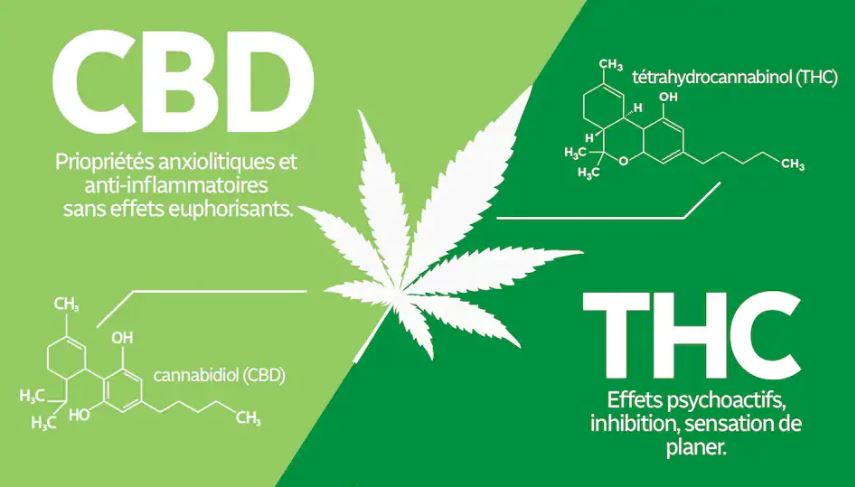
CBD, short for cannabidiol, is the most abundant non-psychoactive cannabinoid in the cannabis plant after THC. It is often used for its medicinal properties. The cannabis plant contains over 100 different cannabinoids, the two best known of which are THC and CBD. THC is psychoactive and can cause effects such as euphoria and drowsiness, while CBD has no psychoactive effects, but can have calming and anxiolytic properties. Cannabinoids work by binding to cannabinoid receptors in the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce their effects. THC and CBD levels vary depending on the cannabis plant, and marijuana is generally regulated differently from hemp due to their respective THC and CBD levels. It is used to treat a variety of conditions, including anxiety, depression, epilepsy, chronic pain, inflammation and insomnia.
Don’t confuse THC and CBD
THE EFFECTS OF CBD
CBD acts on the human body by binding to cannabinoid receptors of the endocannabinoid system, which is responsible for regulating various physiological functions. CBD acts primarily by modulating receptor function rather than binding directly to them. It can also act on other receptors, such as serotonin and adenosine, to produce its effects. Studies have shown that CBD can help reduce inflammation and pain by acting on cannabinoid receptors present in immune cells. CBD can also help reduce anxiety and depression by modulating neurotransmitter transmission in the brain. CBD can also help reduce seizures in people with epilepsy by acting on cannabinoid receptors in the brain. Current research suggests that CBD may be beneficial for a variety of medical conditions, but more research is needed to fully understand its effects on the body.
There are two types of cannabinoid receptors: CB1 receptors, mainly present in the central nervous system, which are activated by THC and induce a state of euphoria, and CB2 receptors, located in the immune system and having immunomodulatory effects. CB1 and CB2 receptors are coupled to G proteins that transmit different signals throughout the body.
CBD has little impact on CB1 and CB2 receptors, unlike THC, which binds mainly to CB1 receptors. CBD is even a CB1 receptor antagonist, which reduces the sensation of euphoria. CBD acts on other cannabinoid receptors, such as serotonin, a neurotransmitter that influences moods and creates a sense of well-being, and anandamide, which has analgesic functions and a role in the reward system. CBD also activates adenosine receptors, providing an anti-inflammatory effect. Although the therapeutic properties of CBD have not yet been clearly demonstrated, it is used for relaxation and should not be used for medicinal purposes.

CBD oil is one of the most common forms of CBD consumption. It is easy to use and dose, and can be added to food or drinks. CBD oil is also used to relieve anxiety, insomnia, pain and other symptoms.
CBD flower can be used in a variety of ways, such as vaporization, infusion in a hot drink or use in culinary recipes. It can also be smoked or used to make joints. It’s important to note that burning CBD flower can produce toxic substances, and vaporization is considered a safer method for inhalation.
CBD capsules are another practical option for those looking to consume CBD discreetly and precisely. The capsules are precisely dosed and can be easily transported for use on the move.
CBD vaporizers are an option for those who prefer to inhale CBD. CBD vaporizers are easy to use and can offer quick relief for pain and anxiety.
CBD cosmetics are products such as creams, balms and lotions that are applied directly to the skin. They can be used to relieve pain and inflammation locally.
CBD edibles are products such as candy, chocolate and gum that contain CBD. They’re a discreet, easy-to-consume option for those looking to use CBD for relaxation or to relieve stress and anxiety.
In conclusion, there are many ways to use CBD. It’s important to choose the shape that best suits your needs and personal preferences. Before starting to use CBD, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and potential health effects.

WHAT EFFECTS DOES CBD HAVE ON CERTAIN DISEASES AND SYMPTOMS?
CBD is known to have beneficial effects on certain diseases and symptoms, such as epilepsy, chronic pain, anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, Tourette’s syndrome, chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting, and even some forms of cancer. However, it’s important to stress that research into the therapeutic properties of CBD is still ongoing, and scientific evidence is limited in some cases. Patients should therefore consult their doctor before using CBD to treat a specific illness or symptom.
Anxiety: CBD is known for its anxiolytic effects, which help reduce anxiety attacks. These effects are attributable to the activation of adenosine receptors in the brain, which regulate anxiety levels.
Schizophrenia: Unlike THC, CBD has anti-psychotic properties that can help treat schizophrenia. It’s important to note, however, that the use of CBD for this condition must be supervised by a healthcare professional.
Pain relief: CBD has analgesic properties that can reduce the perception of pain. Because of its anti-inflammatory effects, CBD could also be effective in the treatment of inflammation, notably caused by Crohn’s disease.
Nausea: CBD’s antiemetic properties can help combat nausea. This is why it is often used to treat the nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy in cancer patients.
Cancer: Numerous studies are investigating CBD’s anti-tumor properties, which may help slow the growth of cancer cells or destroy them.
Diabetes: CBD could be beneficial in the fight against diabetes and its complications by regulating blood sugar levels and reducing inflammation.
Neurological disorders: CBD is known for its neuroprotective effects, which can protect neurons from damage and cell death. This can be particularly beneficial in the treatment of Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
What’s more, CBD can help combat dependence on certain drugs, such as tobacco and opiates, by reducing withdrawal symptoms and helping patients overcome addiction. However, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional before using CBD to treat an illness or symptom.
LEGALITY OF CBD IN SWITZERLAND
Since 2017, Switzerland has authorized the sale of CBD-containing products on condition that their THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) content is less than 1%. This decision paved the way for a multitude of CBD-based products on the Swiss market, such as oils, capsules, creams and dried flowers.
Swiss consumers can buy these products in specialist stores, online or even in supermarkets. However, the Swiss authorities have introduced strict regulations to guarantee consumer safety and avoid any confusion between products containing THC and CBD.
The legality of CBD in Switzerland has also had a positive impact on the local industry, with the creation of Swiss companies specializing in the production and sale of CBD products. However, it’s important to note that CBD regulations can vary from country to country, and consumers should always check local laws before purchasing or consuming CBD products.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, CBD is a promising natural compound for treating a variety of ailments. While research into its therapeutic benefits is still ongoing, it’s important to note that CBD should not be considered a miracle cure for all diseases. Before using CBD, it’s important to talk to a healthcare professional to make sure it’s safe and appropriate for you.

